Welcome to your all-inclusive guide on why your back hurts when you cough. As someone who has vast experience in health and wellness, I understand how alarming and uncomfortable this can be. This article will provide you with valuable insights into why this happens and what you can do about it. Trust me when I say, you are not alone in this, and the information here could just be the relief you’ve been looking for.
So, what exactly causes back pain when you cough? The simple answer is that this discomfort can be due to a variety of issues such as muscle strain, ligament sprain, spinal stenosis, or even a herniated disc. These problems can become aggravated during coughing due to the pressure and sudden movements involved. However, there are ways to manage and possibly alleviate this pain through certain exercises, posture corrections, and non-surgical treatments. Let’s delve deeper into this topic and find out how you can reclaim your comfort and well-being.
What is the Connection Between Coughing and Back Pain?
When you cough, your body experiences a sudden, forceful movement which can strain or stress the muscles and ligaments in your back. This is why your back may hurt when you cough. The pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp sting, depending on the severity of the strain or the underlying condition causing it. It’s important to understand this connection to effectively manage or prevent the discomfort.
The body’s natural response to coughing involves tightening the abdominal muscles. This action puts pressure on the spine, which can exacerbate existing issues or create new ones, particularly if the coughing is chronic. For instance, if you already have a herniated disc, the increased pressure can push the disc further out of place, leading to more severe pain.
According to recent research, chronic coughing can indeed lead to significant musculoskeletal problems. A study found that 38% of patients with chronic cough experienced back pain. This statistic highlights how common this issue can be for those who frequently cough, emphasizing the need for awareness and effective management strategies.
Common Reasons for Back Discomfort When Coughing
Back pain during coughing can be attributed to several factors. These range from simple muscle strain due to the sudden, forceful motion of a cough to more complex underlying health conditions that might be aggravated by the pressure exerted during a cough.
Muscle Strain
Muscle strain or sprain is one of the most common reasons for back discomfort when coughing. This occurs when the muscles and ligaments in your back are overstretched or torn due to the sudden, forceful motion of a cough. Symptoms can include pain that worsens with movement, muscle cramps or spasms, and decreased range of motion.
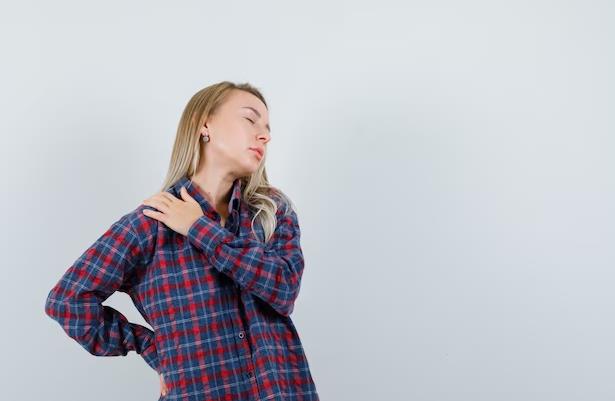

Back Hurts When I Cough: Exploring Causes and Solutions
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc, also known as slipped or ruptured disc, can cause severe back pain that is exacerbated by coughing. This condition occurs when the soft cushion between your vertebrae pushes out through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. The herniated disc can then press on the nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in your back.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition where the spaces within your spine narrow, which can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. Coughing can increase this pressure, leading to intensified pain.
Other Underlying Conditions
Other underlying conditions such as kidney stones, infections, or tumors could also cause back pain when coughing. These conditions might not directly relate to the spine or back muscles but can cause referred pain that is felt in the back.
Understanding these common causes can help you identify the possible reason behind your back discomfort when coughing and guide you towards the appropriate treatment or management strategy.
How to Identify Serious Underlying Issues
When your back hurts while coughing, it’s often due to a simple muscle strain or sprain. However, persistent, severe, or worsening pain could indicate more serious underlying issues such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or even a tumor. Recognizing the signs of these conditions can help you seek timely medical attention and prevent further complications.
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc can cause intense pain in your back, especially when coughing. The pain often radiates down one leg and may be accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness in the leg. You might also experience pain when sitting, standing for long periods, or during certain movements.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition that causes the spaces within your spine to narrow, putting pressure on the nerves. Symptoms include back pain that worsens with walking or standing and improves when you lean forward or sit. Coughing can exacerbate the pain due to the increased pressure on the spine.
Tumors
Though rare, tumors in the spine can cause back pain when coughing. The pain is often persistent and does not improve with rest. Other symptoms may include unexplained weight loss, changes in bowel or bladder function, or a decrease in muscle strength.
Understanding the symptoms of these serious conditions can guide you in seeking appropriate medical attention. If you experience any of these symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve your prognosis and quality of life.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Back Pain Aggravated by Coughing
While persistent back pain during coughing is a cause for concern, it’s also important to note that there are several non-surgical treatments available to alleviate discomfort. These methods aim to reduce inflammation, relax tense muscles, and improve your overall back health.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists can teach you exercises and techniques to improve your posture, strengthen your back and abdominal muscles, and increase your flexibility. They can also use methods like massage, heat or cold therapy, and electrical stimulation to help manage your pain.
Over-the-Counter Medication
Non-prescription medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Prescription Medication
For severe pain, your doctor might prescribe stronger pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or even injections of corticosteroids or numbing medication.
Lifestyle Changes
Losing weight, quitting smoking, and getting regular physical activity can help improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing back pain. Avoid heavy lifting when possible, and make sure to lift properly when you can’t avoid it.
Remember, while these methods can provide relief, they should not replace a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional if you are experiencing severe or persistent back pain when coughing. Always consult with a medical expert to ensure you’re taking the right steps towards recovery.
Exercises and Posture Corrections to Alleviate Back Pain
The discomfort experienced in your back while coughing can be alleviated through certain exercises and posture corrections. These techniques can help strengthen your back muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce the strain on your spine, thereby reducing the pain you feel when you cough.
Exercises to Alleviate Back Pain
-
Pelvic Tilts: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles and push your lower back into the floor. Hold for a few seconds, then relax. Repeat this exercise 10 times.
-
Cat-Camel Stretch: Get on your hands and knees. Arch your back like a cat, then sag it down like a camel. Do this stretch 10 times.
-
Partial Crunches: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Cross your arms over your chest and lift your shoulders off the floor. Keep your stomach muscles tight and avoid using your hands or neck to pull yourself up. Repeat 10 times.
Posture Corrections to Alleviate Back Pain
-
Standing Posture: Stand up straight with your shoulders back, abdomen in, and the small of your back curved inwards. Your weight should be evenly distributed on both feet.
-
Sitting Posture: Sit with your back straight and shoulders back. Your buttocks should touch the back of your chair, and your feet should be flat on the floor.
-
Lifting Posture: When lifting objects, bend at your knees, not your waist. Keep the object close to your body and avoid twisting your body while lifting.
Remember, these exercises and posture corrections are meant to alleviate back pain, not exacerbate it. If any movement causes sharp or severe pain, stop immediately and consult a healthcare professional. Regularly incorporating these exercises and maintaining correct posture can go a long way in managing your back pain and improving your overall quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Persistent Back Pain
While occasional back pain when coughing is common and usually not a cause for concern, persistent or severe back pain warrants medical attention. It’s crucial to listen to your body and recognize when the pain is more than just a minor annoyance. Persistent back pain could be an indication of a serious underlying condition that needs immediate medical intervention.
There are several signs to watch out for that indicate the need to seek medical attention. These include intense pain that doesn’t improve with rest, pain that radiates down one or both legs, loss of bladder or bowel control, unexplained weight loss, and fever. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms along with your back pain, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
In addition, if your back pain is due to an injury or a fall, or if it’s accompanied by numbness or tingling, you should also seek medical help. It’s always better to be safe and get a proper diagnosis rather than ignoring the symptoms and potentially allowing the condition to worsen. Remember, early detection and treatment can greatly improve the prognosis of most health conditions.
Conclusion
Back pain when coughing is not an uncommon occurrence and is often the result of simple muscle strain caused by the forceful motion of a cough. However, persistent or severe back pain could indicate more serious underlying conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or even tumors. Understanding the connection between coughing and back pain, and recognizing the signs of serious underlying conditions, can guide you in seeking appropriate medical attention.
Remember, while non-surgical treatments and lifestyle changes like exercises and posture corrections can provide relief, it’s always better to consult with a healthcare professional if you’re experiencing severe or persistent back pain. With the right knowledge and treatment, you can manage your back pain effectively, continue to enjoy your daily activities, and maintain a high quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
[faq-schema id=”1212″]