East Africa faces significant healthcare challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, limited access to medical services, and a shortage of healthcare professionals. To address these issues, a multifaceted approach is required, focusing on improving healthcare infrastructure, leveraging technology, and enhancing workforce training. By implementing these strategies, East Africa can make substantial progress in providing quality healthcare to its population. This article explores the necessary steps to overcome these challenges and build a robust healthcare system in the region.
Improving healthcare infrastructure is crucial for addressing the region’s healthcare challenges. Many healthcare facilities in East Africa are outdated and lack essential equipment. Investing in modernizing these facilities is a priority. This includes upgrading hospitals, clinics, and health centers to ensure they are equipped with the necessary tools and technology to provide quality care. Additionally, building new healthcare facilities in underserved areas can help bridge the gap in access to medical services.
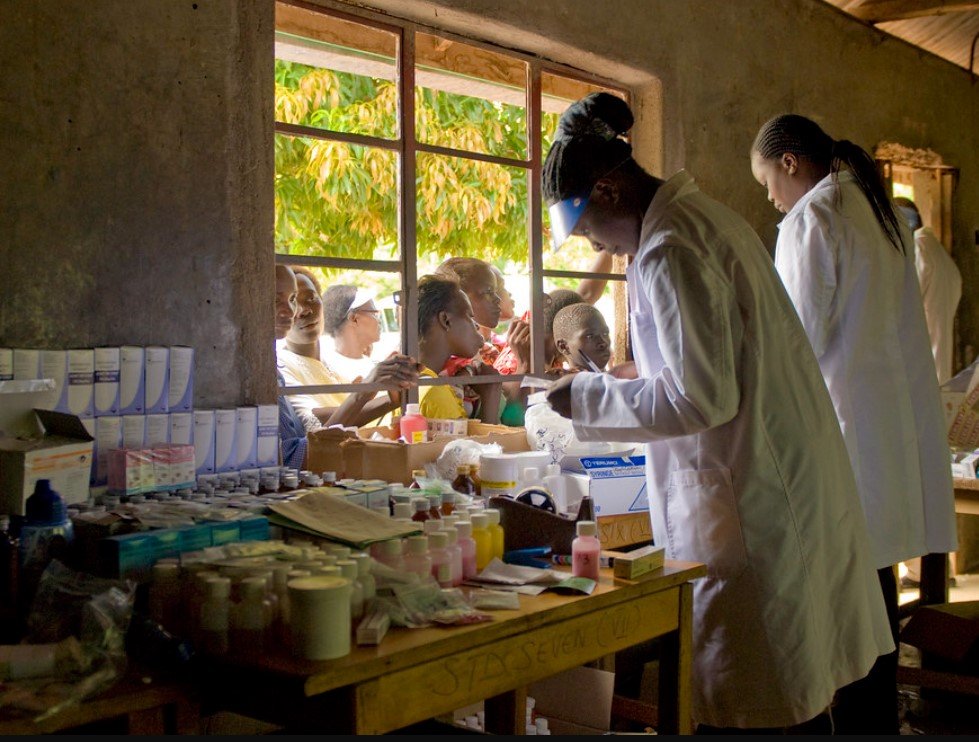
Another critical aspect is ensuring a reliable supply chain for medical supplies and equipment. Many healthcare facilities face shortages of essential medicines and medical devices. Establishing efficient supply chain management systems can help mitigate these issues. This involves working with local and international suppliers to ensure a steady flow of medical supplies. Furthermore, implementing robust maintenance programs for medical equipment can prevent breakdowns and ensure continuous operation.
Leveraging Technology for Better Healthcare
Technology plays a vital role in transforming healthcare delivery in East Africa. The rise of eHealth and telemedicine offers new opportunities to improve access to medical services. Telemedicine allows patients in remote areas to consult with healthcare professionals without the need for travel. This can significantly reduce the burden on healthcare facilities and provide timely medical advice to those in need. Additionally, electronic health records (EHRs) can streamline patient information management, making it easier for healthcare providers to access and share patient data.
Mobile health (mHealth) initiatives are also gaining traction in the region. These programs use mobile phones to deliver health information and services to patients. For example, mHealth applications can provide reminders for medication adherence, schedule appointments, and offer health education. By leveraging the widespread use of mobile phones, these initiatives can reach a large portion of the population and improve health outcomes. Moreover, integrating big data analytics can help identify health trends and inform public health strategies.
Strengthening the Healthcare Workforce
A well-trained and adequately staffed healthcare workforce is essential for delivering quality care. East Africa faces a significant shortage of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and specialists. Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach. Firstly, increasing investment in medical education and training programs is crucial. This includes expanding medical schools, offering scholarships, and providing continuous professional development opportunities for healthcare workers.
Secondly, improving working conditions and offering competitive salaries can help retain healthcare professionals in the region. Many healthcare workers leave for better opportunities abroad due to poor working conditions and low pay. By addressing these issues, East Africa can retain its talent and ensure a stable healthcare workforce. Additionally, implementing task-shifting strategies, where certain medical tasks are delegated to trained community health workers, can help alleviate the burden on healthcare professionals and improve service delivery.
Promoting Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives are vital for preventing diseases and promoting overall health in the community. Vaccination programs, health education campaigns, and preventive screenings can significantly reduce the incidence of communicable and non-communicable diseases. Collaborating with international organizations and leveraging funding from global health initiatives can support these programs. Additionally, addressing social determinants of health, such as access to clean water, sanitation, and nutrition, is essential for improving health outcomes.
Community engagement is also crucial for the success of public health initiatives. Involving local communities in health programs can increase awareness and participation. This includes training community health workers to deliver health education and services at the grassroots level. By empowering communities, East Africa can build a sustainable and resilient healthcare system that addresses the unique needs of its population.
















