Researchers have developed a groundbreaking method to print thin metal oxide films at room temperature, resulting in transparent, flexible, and highly conductive circuits. This innovative technique uses liquid metal to deposit solid oxide films that maintain their conductive properties even at high temperatures. The development promises to revolutionize the electronics industry by enabling the creation of flexible devices and circuits on unconventional surfaces. This article delves into the details of this new technique, its potential applications, and the future of flexible electronics.
The Breakthrough in Metal Oxide Printing
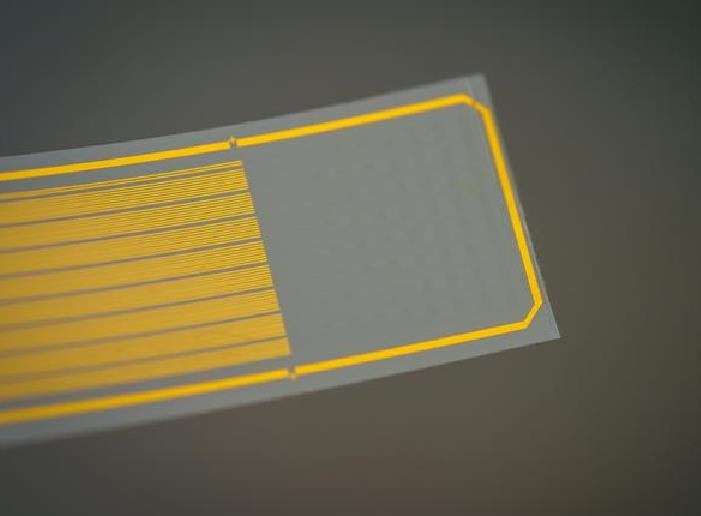
The new metal oxide printing technique represents a significant advancement in the field of electronics. Traditionally, creating metal oxides for electronic applications required specialized equipment that operated at high temperatures and was both slow and expensive. This new method, however, allows for the creation and deposition of metal oxide thin films at room temperature, making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
The technique involves filling the space between two glass slides with liquid metal, creating a small meniscus that extends beyond the ends of the slides. This meniscus is covered with a thin metal oxide skin that forms where the liquid metal meets the air. By moving the meniscus across a surface, the metal oxide on the front and back of the meniscus sticks to the surface and peels off, similar to the trail left by a snail. This continuous process allows for the printing of metal oxide films that are both transparent and flexible.
One of the key advantages of this technique is its ability to produce metal oxide films that maintain their conductive properties even at high temperatures. This makes them ideal for use in a wide range of electronic devices, from touch screens and displays to sensors and wearable technology. The flexibility of the films also opens up new possibilities for integrating electronics into everyday objects, such as clothing and packaging.
Potential Applications of Flexible Electronics
The development of transparent, flexible metal oxide films has the potential to transform various industries by enabling the creation of innovative electronic devices. One of the most promising applications is in the field of wearable technology. Flexible circuits can be integrated into fabrics, allowing for the development of smart clothing that can monitor health metrics, track physical activity, and even provide haptic feedback.
Another exciting application is in the realm of flexible displays. Traditional displays are rigid and fragile, but flexible metal oxide films can be used to create bendable screens that are more durable and versatile. These screens could be used in a variety of devices, from smartphones and tablets to foldable laptops and rollable televisions. The ability to create flexible displays also opens up new possibilities for interactive advertising and digital signage.
In addition to consumer electronics, flexible metal oxide films have potential applications in the medical field. For example, they can be used to develop flexible sensors that can be applied directly to the skin to monitor vital signs or detect biomarkers. These sensors could provide continuous, real-time health monitoring, improving patient care and enabling early detection of medical conditions. The flexibility and transparency of the films also make them suitable for use in implantable medical devices, where they can conform to the body’s contours and provide unobtrusive monitoring.
The Future of Flexible Electronics
The new metal oxide printing technique is poised to drive significant advancements in the field of flexible electronics. As researchers continue to refine the process and explore new applications, the potential for innovation is vast. One area of ongoing research is the development of more complex circuits and devices using the printed metal oxide films. By combining multiple layers of films and integrating different types of electronic components, researchers aim to create fully functional, flexible electronic systems.
Another area of interest is the environmental impact of the new technique. Traditional methods of creating metal oxides often involve toxic chemicals and generate significant waste. The new room-temperature printing method is more environmentally friendly, as it reduces the need for harmful substances and minimizes energy consumption. This makes it a more sustainable option for the production of electronic devices.
The commercialization of flexible electronics is also on the horizon. As the technology matures and becomes more cost-effective, it is likely to see widespread adoption in various industries. Companies are already exploring ways to incorporate flexible electronics into their products, from consumer gadgets to industrial equipment. The ability to create transparent, flexible circuits will enable new designs and functionalities, driving innovation and enhancing the user experience.
















