Internal medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of diseases and conditions affecting adults. Internal medicine doctors, also known as internists, are often called the “generalists” of the hospital, as they care for patients with complex and diverse medical problems, and coordinate their care with other specialists. Internal medicine is an essential and challenging field that requires a high level of knowledge, skill, and compassion.
Internists are trained to provide comprehensive and holistic care for patients in various settings, such as outpatient clinics, emergency rooms, intensive care units, and wards. Internists can also subspecialize in different areas of internal medicine, such as cardiology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, hematology, infectious diseases, nephrology, pulmonology, rheumatology, and more.
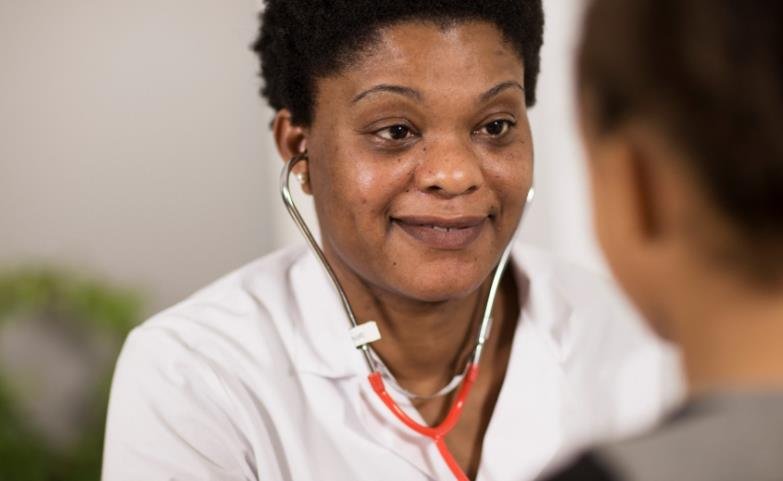

Internists are responsible for managing the health and well-being of their patients, from prevention and diagnosis, to treatment and follow-up. Internists perform physical examinations, order and interpret tests, prescribe medications, perform procedures, and consult with other doctors. Internists also educate and counsel their patients on their health issues, and help them make informed decisions about their care.
Why are internists important?
Internists are important for several reasons, such as:
- Internists are experts in dealing with complex and chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, kidney disease, lung disease, and more. Internists can handle multiple and overlapping problems, and provide integrated and coordinated care for their patients.
- Internists are leaders and collaborators in the hospital, as they work closely with other specialists, nurses, pharmacists, social workers, and other health care professionals. Internists can communicate effectively and efficiently, and ensure that the patient’s needs and preferences are met.
- Internists are advocates and educators for their patients, as they empower them to take charge of their health and wellness. Internists can explain complex medical information in simple and understandable terms, and help their patients navigate the health care system and access the resources they need.
- Internists are innovators and researchers in the field of medicine, as they contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge and practice. Internists can conduct clinical trials, publish scientific papers, and develop new guidelines and protocols for improving the quality and safety of patient care.
How to become an internist?
To become an internist, one has to complete a rigorous and demanding training program, which includes:
- Four years of medical school, where one learns the basic sciences and clinical skills of medicine.
- Three years of residency in internal medicine, where one gains hands-on experience and expertise in caring for adult patients in various settings and specialties.
- Optional one to three years of fellowship in a subspecialty of internal medicine, where one develops further knowledge and skills in a specific area of interest and practice.
To practice as an internist, one has to obtain a license from the state medical board, and pass the board certification exam from the American Board of Internal Medicine. One also has to maintain their certification and license by completing continuing medical education and meeting the professional standards and ethics of the field.
Internal medicine is a rewarding and fulfilling career that offers many opportunities and challenges for those who are passionate about caring for adult patients and improving their health outcomes. Internal medicine is also a vital and indispensable part of the health care system, as internists play a key role in providing quality and cost-effective care for the population.